What is diabetes?
Diabetes is caused when insulin isn’t made enough, or any, by the pancreas. When insulin isn’t made enough, we cannot control blood sugar.
There are two main types of diabetes: Type 1 patients need to take insulin every day to stay alive, and type 2 that is caused by insulin resistance, a condition in which the body’s cells cannot use insulin as efficiently as normal.
Type 2 diabetes
90% of patients who develop diabetes have this type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is a disease in which the amount of glucose in the blood becomes higher than normal due to insufficient secretion of insulin in the pancreas. In the past, most of the cases occurred after the age of 40, but diabetes diagnoses among youth are becoming more common because of the high proportion of fat in our diet.
Due to high-calorie and / or high-fat diet, lack of exercise, and constitution, insulin secretion by the pancreas decreases. Insulin, which is made by the pancreas, originally works to lower blood glucose (blood sugar) levels, but in type 2 diabetes, insulin secretion is insufficient, making it impossible to control blood glucose levels.
Type 2 diabetes can be controlled with lifestyle, such as healthy eating and exercising, and taking insulin when insulin is either insufficient or ineffective. However, if you cannot control your blood sugar level with your medication, you will need insulin injections.
Type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes usually appears before the age of 40, and accounts for 10% of all people with diabetes. While type 2 diabetes can be controlled with improving lifestyle, type 1 diabetes has nothing to do with diet or lifestyle.
When you have type 1 diabetes, you cannot produce any insulin, so insulin injection will be unavoidable. Without insulin, your body will break down its own fat and muscle, leading to a serious condition called diabetic ketoacidosis. If left untreated, people die quickly, so you need to rely on insulin injection for survival.
When you don’t manage your diabetes and control your blood sugar, complications occur. Some of the common complications are: kidney disease, heart disease, stroke, eye disease, and high blood pressure. It is important to take insulin regularly to control blood sugar.
The cause of diabetes
What is blood sugar?
Blood sugar comes from the food you eat. Your body creates blood sugar by digesting some food into a glucose that circulated in your bloodstream. Most of the digested food is then absorbed by the small intestine to be used as energy, and the excess glucose will be converted to fat. The key to this process is insulin.
How insulin works
Insulin is released from your pancreas and plays a role in sending glucose in your bloodstream. The pancreas detects the rise in blood glucose and starts to secrete insulin. Insulin works by improving the uptake of glucose from the blood into the cells of body, and takes glucose out of the bloodstream. Once the glucose is used as the energy to fuel the cells, glucose level drops.
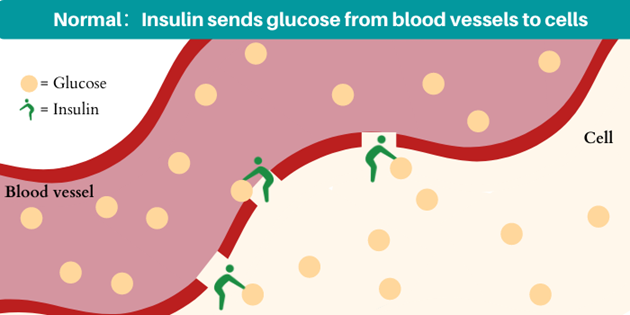
What happens when your insulin levels drop?
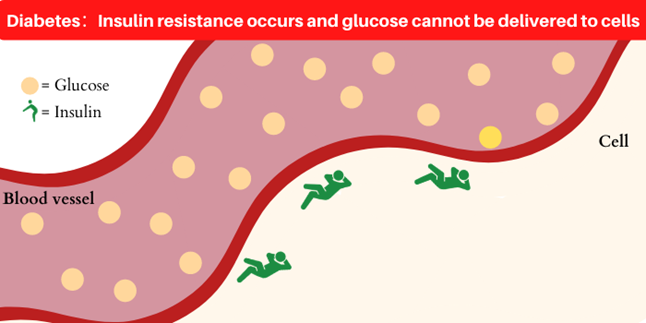
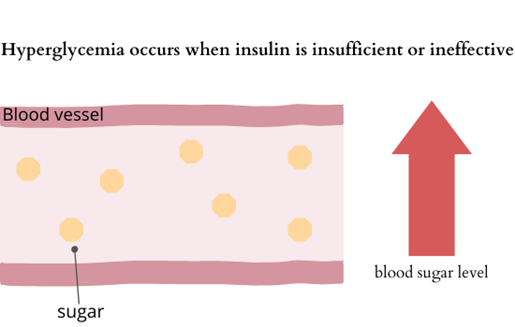
When insulin, which plays an important role in delivering glucose to cells, is not sufficiently secreted or fails to function properly, the body can no longer move glucose from the blood into the cells, causing high blood glucose levels. When the glucose level is too high, excess glucose will be removed from the body along with urine.
Type 2 diabetes can be caused when the available insulin doesn’t work properly. Even though insulin is secreted, the action is impaired.
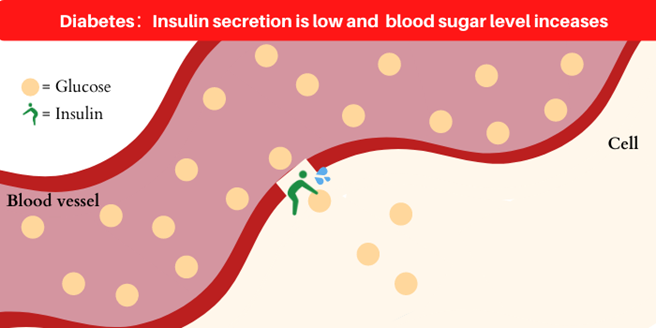
On the other hand, type 1 diabetes produce very little or no insulin at all. When impaired insulin secretion, glucose will not be delivered to cells and remains in the bloodstream, resulting in hyperglycemia.
When the blood sugar becomes too high, the pancreas tries hard to make insulin, but the pancreas itself weakens and gradually becomes tired. Then, amount of insulin decreases, resulting in an increase in blood sugar.
Early signs and symptoms of diabetes
Type 2 diabetes often has almost no subjective symptoms at the early stage, and most people cannot notice it. However, it is said to occur easily in the following people:
- 40 years or older
- Overweight
- Family member has diabetes
- Lack of exercise
Also, if you are aware of the following symptoms, which are often listed as the initial symptoms, it is highly possible that the condition has already progressed to some extent.
- Feeling very tired
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst and hunger
- Blurry vision
- Slow healing of wounds
- Numbness or pain in the hand or feet
- Itching and yeast infections
- Sexual function problem
Diabetes are often pointed out by blood tests, so having a health checkups can be an effective preventive measure.
Diabetes prevention
When it comes to type 2 diabetes, prevention is very important. Nearly one-third of adults are at risk of developing type 2 diabetes, so try to improve your lifestyle before you have them. Prevention listed often are as basic as eating healthier, becoming more physically active and losing a few pounds. Except for the above-mentioned measures against diabetes, managing blood pressure and controlling blood sugar level is important.
Manage blood pressure
High blood pressure causes poor blood flow, which causes the heart and the brain from getting enough oxygen and nutrients to function properly. If there is ROS, oxidative stress increases, inflammation in blood vessels occurs, and the function of the pancreas reduces.
Even when blood pressure is very high, it often causes no symptoms at all and that’s why people may live with it unknowingly for a long time. It is important to maintain proper weight and reduce salt intake at the same time.
Control blood sugar
When the function of the pancreas decrease, the amount of insulin production becomes insufficient. Also, obesity due to overeating and lack of exercise interferes with insulin. When the resulting hyperglycemia continues, the risk of heart disease and stroke increases by 2 to 4 times. It is necessary to control the blood sugar level to prevent complications.
Risk of developing diabetes
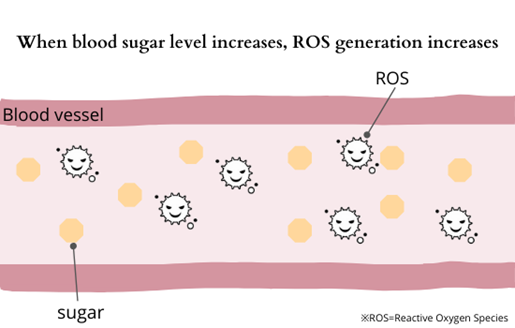
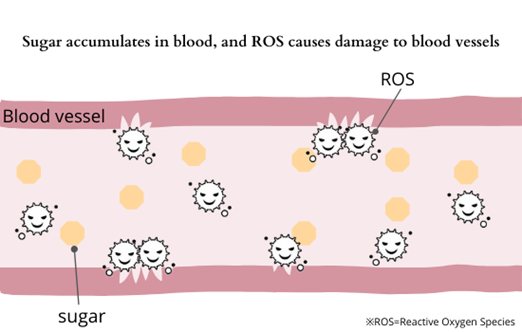
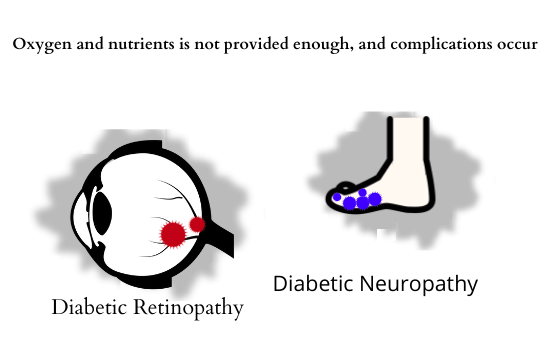
Complications of diabetes
If blood sugar levels are continued to be very high, it can cause problems with other body functions. The longer you have diabetes, the higher the risk of complications. Eventually, diabetes complications may be disabling or even life-threatening. Possible complications include:
- Eye damage (retinopathy)
The retina is a thin lining on the back of the eye, and when high blood sugar is kept from diabetes, blood flow becomes poor. You may not have any signs at first, but as it worsens, blood vessels weaken and leak blood and fluid. This causes blocks in your vision and may cause blindness.
- Kidney damage (nephropathy)
Diabetic nephropathy affects your kidneys’ ability to remove waste from your body. Severe damage can lead to kidney failure or irreversible end-stage kidney disease, which may require dialysis or kidney transplant. If you start to have dialysis treatments for your whole life unless you are able to get a kidney transplant.
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
Long-term hyperglycemia are critical for peripheral nerve damage, resulting in excessive sweating, irregular bowel movements, and erectile dysfunction in men may also occur. If left untreated, the damage caused by neuropathy can potentially lead to infection and limb amputation.
- Cardiovascular disease
People with diabetes are three times more likely to have heart attack or stroke than people without it. Both strokes and heart attacks can occur due to blocked arteries. Over time, high blood glucose from diabetes can damage your blood vessels and the nerves that control both your heart and blood vessels. Atherosclerosis clogs your arteries blocking nutrients to reach the cells. The cells in brain and heart cannot be repaired or regenerate, which causes serious sequelae. Depending on where it occurs, heart attack deaths occur within 10 minutes, and stroke can cause weakness or paralysis on one side of the body, or worse, the whole body.
What is the cause of insulin deficiency?
At an early stage, it is possible to get your blood glucose level back to normal range with lifestyle modifications such as eating a healthier diet, exercising more, or reduce the amount of insulin by taking oral pills that increase the release of insulin from the pancreas.
However, type 1 diabetes cannot make insulin, so they must inject insulin to control their blood glucose levels.
Lack of insulin in the body, cells can no longer take up glucose from the blood, and the blood glucose level increases. Poor glycemic control declines renal function, leading to rental failure. Patients with stage 3 chronic kidney disease will undergo dialysis treatments in about two years, and heart attack is the most common cause of death among people on dialysis. On average, life expectancy after initiation of dialysis is approximately eight years.
The root cause is ROS (reactive oxygen species), which reduces insulin secretion by the pancreas.
Solution to Diabetes
What is ROS (reactive oxygen species)?
Oxygen taken in by the body combines with hemoglobin in the blood and is carried to cells in each tissue of the body. While moving in the blood, oxygen becomes ROS due to the effects of stress, disorderly oxidized surrounding cells and cholesterol. ROS is generated in the blood due to lack of exercise, unbalanced diet, stress, and smoking, and those generate oxidative stress that causes aging, high blood pressure, arteriosclerosis, heart attack, and stroke.
Relationship between ROS and aging
When cells are attacked by ROS, lipids in the cell membranes of blood vessels are oxidized, blocking the blood vessels. When a blockage of the blood vessels happen, nutrients cannot be sent to the body tissues, and tissue waste cannot be taken away. Also, damage to vascular cells lead to death of vascular cells and oxidation of LDL cholesterol in the blood to form a hard layer inside blood vessels. This accelerates aging of blood vessels as arteriosclerosis and high blood pressure.
In this way, ROS damages or destroys cells, which promotes aging of the entire body and gradually causes heart attack, stroke, or cancer.
Suppressing ROS can prevent type 2 diabetes
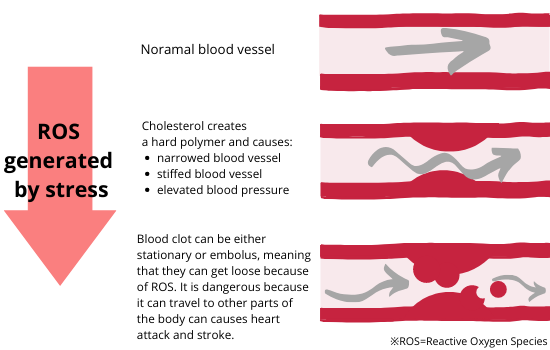
When excessive amount of ROS is generated in the blood, it attacks the cells of blood vessels, blocks blood flow, which causes blockage inside. The blockage reduces blood flow, reducing nutrients and energy being supplied to the entire body. ROS also affects the pancreatic function that secretes insulin.
The beta cells in the pancreas secrete insulin, but since these beta cells are very weak to ROS, if the ROS is supplied to the pancreas by the blood, the vitality of beta cells will be lost and the amount of insulin secretion will decrease resulting in high blood sugar.
As described, diabetes and ROS are closely related, and suppression of ROS is the key to improving diabetes by activating the function of the pancreas without any control of insulin.
Diabetes can be prevented by suppressing ROS, which results in preventing arteriosclerosis and blockage, and improving the vitality of cells of the pancreas to normalize insulin secretion.
NOMOA
-The world’s only technology that succeeded in suppressing the occurrence of ROS without medications-

In 2010, NOMOA was announced as the world’s first successful study to physically suppress ROS in the blood at the World Pharmaceutical Congress held in Copenhagen, Denmark. This was a result of a joint research by Dr. Yamamoto, Dr. Koike, Dr. Yonehara of the Faculty of Pharmaceutical Science of Ohu University in Fukushima, Japan, and Dr. Kumano.
This study first took nine volunteers’ blood and measured the level of oxidative stress (ROS / dROM) and immunity (BAP) in the blood. Then, they put their index finger into the device for 10 minutes. After the blood circulation, it was sampled again to measure both oxidative stress level and immunity. As the result, it was confirmed that all nine volunteers’ level of ROS decreased, and immunity (BAP) did not show any decline.
From this, it was confirmed that the NOMOA suppressed ROS in the blood, and that it had no effect on immunity.
To test the effects of sleep-inducing effects on animals, we have prepared NOMOA that can fit the whole body of a mouse.
First, we measured the amount of activity with a sensor, which was activated each time the mouse moved in the cage. Then, the mouse was placed in NOMOA for 10 minutes and put back in the cage and measured the amount of activity. The test was automatically measured for each two mice for 23 hours.
The average amount of activity per minute of the mouse was 52.7 point, whereas the amount of activity of the NOMOA-affected mouse was 48.7 points per minute on average, which was decreased by 7.6%. From this, it was demonstrated that the NOMOA-treated mice had a longer duration of behavioral arrest. This can be said to have caused drowsiness in mice and induced sleep when the oxidative stress level (active oxygen level) in blood is suppressed.
It is also proved that the action of NOMOA suppresses ROS in the blood and prevents disease caused by ROS, such as diabetes, arteriosclerosis, high blood pressure, heart attack, and stroke. Also, it helps to eliminate sleep disorders caused by oxidative stress.
In July 2018, we have presented the world’s first research to lower blood pressure physically without using any medications with wrist-type NOMOA at the World Congress of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology in Japan. In the test, a control, magnet, and NOMOA were worn in turns for 24 hours on 19 volunteers with a blood pressure meter that is capable to measure continuously for 24 hours.
The blood pressure of all 19 NOMOA-treated volunteers decreased by an average of about 5 mmHg compared to the controls and magnets.
From the results from both studies, it was proved that the use of NOMOA can suppress ROS, which causes diabetes, and also lower blood pressure.