What’s erectile dysfunction (ED)?
Erectile dysfunction is when a man has difficulty getting an erection or keeping it long enough for sex. Not only cases where erection does not occur, but also cases where erection is not enough to have satisfied sex, such as insufficient hardness and inability to get and keep erection.
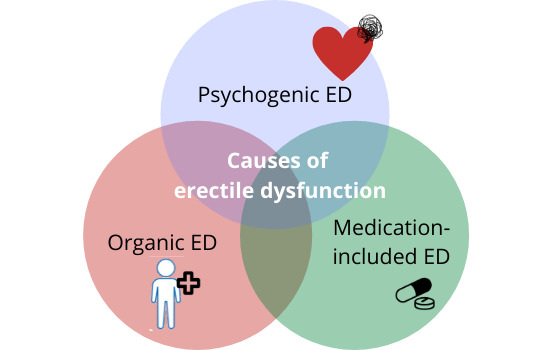
Causes of ED
Sometimes erectile dysfunction only occurs in certain situations. For example, you may be able to get an erection during masturbation, or you may find that you sometimes wake up with an erection but you are unable to get an erection with your sexual partner.
If this is the case, it is likely the underlying cause of erectile dysfunction is psychological (stress related). If you are unable to get an erection under any circumstances, it is likely that the underlying cause is physical. Knowing the cause is essential for the cure.
Physical cause
Arteriosclerosis, nerve damage, narrowing of blood vessels
Erectile dysfunction is all about blood flow. To get and keep an erection, blood needs to have no problem getting to your penis. If you have erectile dysfunction, it can mean that one or more of your blood vessels have narrowed or are blocked. Plaque in your arteries, atherosclerosis, can make that happen.
Most men with erectile dysfunction have risks that make them more likely to get atherosclerosis, such as diabetes and high blood pressure.
Even in diseases such as cerebral hemorrhage and dementia that damage nerves can be the cause of erectile dysfunction since the signal of sexual stimulation captured by the brain does not reach.
Problems with blood vessel functions, including diabetes and high blood pressure
When diabetes and high blood pressure continues, blood vessels age more quickly than usual. When vessels are worn out, it does not dilate sufficiently even if there is a sexual stimulation.
Poorly controlled blood sugar levels can damage small blood vessels and nerves. Damage to the nerves that control sexual stimulation and response can impede a man’s ability to achieve an erection firm enough to have sexual intercourse. Reduced blood flow from damaged blood vessels can also contribute to erectile dysfunction.
On the other hand, even if your blood sugar is not too high, blood vessels tend to age due to other factors, such as lifestyle-related diseases, that may lead to erectile dysfunction, such as people with high blood pressure and high cholesterol, smoking and excessive drinking.
Side effects of medications
Some medications can cause erectile dysfunction regardless of age.
- Central nervous system medications: antidepressants, anxiolytics, antipsychotics
- Peripheral neuropathy medications: anesthetics, anticonvulsants
- Cardiovascular medications: diuretics, antihypertensive drug, vasodilators, cholesterol medications
- Gastrointestinal disorders medications: peptic ulcer, anticonvulsants, anticholinergic
blood vessels or nerves may be damaged due to surgery or accidents
Well-known causes of erectile dysfunction are arteriosclerosis, aging, and life-style as mentioned above, but erectile dysfunction may also be caused by an accident or surgery. Other than damage to the penis itself, damage to nerves and blood vessels can be the reasons. Spinal cord injuries and pelvic fractures, in particular, contain many fine nerves and blood vessels, so are more likely to cause erectile dysfunction.
Psychological cause
Most people in their 30s and 40s have psychological issues. Some of the most common causes of psychological impotence include the following:
- Stress
- Anxiety
- Relationship problems
- Depression
- Performance anxiety
- Guilt
- Low self-esteem
If they have anxiety and stress, it can affect the brain’s ability to send the necessary signals to trigger the desired physical response – an erection. Stress and anxiety can also contribute to an ongoing cycle of erectile dysfunction, including hormones, muscles, blood vessels, nervous system and emotions.
When thinking of depression, many think as something akin to sadness. However, depression includes frustration, loss of interest, low self-esteem, or guilt.
Treatment
Psychological counseling
If erectile dysfunction is caused by stress, anxiety or depression – or the condition is creating stress and relationship tension – your doctor might suggest to visit a psychologist or counselor. Also, relationship problems causing stress can lead to struggling in the bedroom. Communication is the first step in resolving this particular cause for psychological erectile dysfunction, but it is also one of the most difficult steps to take. If communicating with your partner is difficult, there’s always couples counseling.
Medications
| Product name | Viagra | Levitra | Cialis |
| Common name | Sildenafil | Vardenafil | Tadalafil |
| Duration | < 10 hours | < 10 hours | 36 hours |
| Time of taking to peak effect | 60 minutes | 30-60 minutes | 60 minutes |
| Existence of generic | ○ | × | × |
Treatment with medications is performed after removing lifestyle-related diseases and psychologically related factors. The three most popular erectile dysfunction treatments on the market are Viagra, Levitra and Cialis. All three treatments provide the same key benefit – better blood flow to the penis and fewer difficulties developing an erection. However, they also have some differences, ranging from duration of effectiveness to different side effect profiles.
Testosterone replacement therapy
As a man ages, the amount of testosterone in his body naturally gradually declines. This decline starts after age 30 and continues throughout life. Without adequate testosterone, a man may lose his sex drive, experience erectile dysfunction, feel depressed, have a decrease sense of well-being, and have difficulty concentrating.
Testosterone replacement therapy is effective for those with mild ED, but not moderate and severe ED.
Solving the fundamental cause
As mentioned earlier, erectile dysfunction is caused by poor blood flow. Men who have arteriosclerosis or clogged arteries in their heart often have the same problem with the arteries that supply the penis with blood. The fundamental cause of arteriosclerosis and clogged arteries is reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Erectile dysfunction is often caused by oxidative polymerization of cholesterol in blood vessels by reactive oxygen species, resulting in clogged blood vessels and poor blood flow. It is often said that cholesterol itself is bad, but when the body becomes oxidized state and the oxidized cholesterol cannot pass through the wall of blood vessel and clings to it, a blood clot occurs. In other words, in order to prevent arteriosclerosis and cholesterol oxidation, it is necessary to suppress the reactive oxygen species.
Side effects and risk of medications
Since erectile dysfunction drugs affect blood vessels in other areas of body, and not just the penis, they can be dangerous when combined with other medications or if you have certain medical conditions. You should think twice about taking erectile dysfunction drugs if you are in following situations.
You take certain medications
Nitrate, medication used to prevent chest pain, should be avoided with erectile dysfunction medications at all cost. Viagra’s side effects, for example, such as nasal congestion and headaches, are minor and unlikely to cause any health issues or significant discomfort. However, Viagra can interact with nitrates, causing serious side effects.
Usually Viagra and other erectile dysfunction medications, Cialis and Levitra, drops blood pressure by a small amount. This drop in blood pressure generally isn’t something to worry about if you’re a healthy person. However, when using Viagra with a nitrate, it can trigger a more severe drop in your blood pressure levels, which could potentially result in loss of consciousness or full-on cardiac arrest.
Even if you do not take nitrate on regular basis, if you have a heart attack during sexual activity, there is a high probability that you will be injected nitrate at a hospital. It is therefore important to inform your partner when using any of the three erectile dysfunction medications as even a healthy person may suddenly have a heart attack.
You’re at risk for heart attack or stroke
Viagra itself is not a drug that adversely affects the heart by dilating blood vessels and lowering blood pressure, but it can be dangerous to take if you have a heart disease. Patients with heart disease, such as angina, severe cardiovascular disease, and heart failure, should keep in mind that sexual activity may not be safe.
For those who have developed heart disease within the past six months are considered unsuitable for taking Viagra since it increases heart rate, blood pressure, and myocardial oxygen consumption during sexual activity. Also, caution is needed, as sexual activity itself carries cardiovascular risks.
Preventive measures
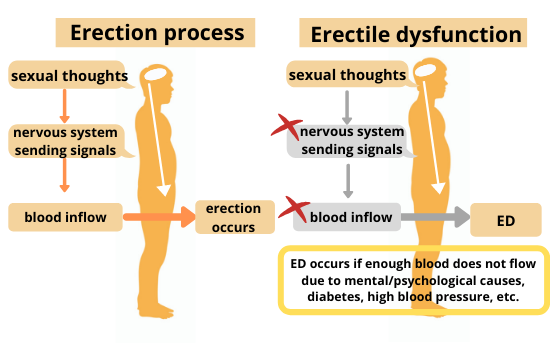
Inadequate arterial dilation results in erectile dysfunction
When sexual stimulation is transmitted from the brain to the penis via nerves, the arteries expand greatly and blood flows into the penis during normal erection. However, arteriosclerosis is a disease in which a mass of cholesterol sticks to the walls of blood vessels, causing the arteries to harden. In other words, arteriosclerosis does not let the arteries to expand, which results in less amount of blood flow for erection.
Arteriosclerosis is the cause
Arteries that become narrow and stiff prevents arteries from widening properly when tissues need more blood. Among many potential consequences, this may make it hard for the penis to get enough extra blood to produce an erection.
Arteriosclerosis not only causes erectile dysfunction, but it also causes serious diseases such as stroke and myocardial infarction. Preventing arteriosclerosis leads to preventing not only erectile dysfunction but other diseases.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) is causing arteriosclerosis
Lifestyle habits such as lack of exercise, drinking, smoking, and bad eating habits generates ROS and oxidizes LDL cholesterol. The oxidized LDL polymerizes and hardens, forming plaque in blood vessels and accumulates in the vessel wall, which clogs arteries.
Since LDL does not oxidize unless ROS is generated, we can see how ROS is affecting our body and is the main cause of arteriosclerosis.
Solution to Erectile dysfunction
What is ROS?
When oxygen is carried into the cells of body tissues, it combines with hemoglobin in blood. While moving inside blood vessels, oxygen can be turned to ROS under stress, high level of cholesterol and disorderly oxidized vascular cells. ROS stem from several factors, including lack of exercise, unbalanced diet, stress and habitual smoking, which all develop oxidative stress that causes aging, high blood pressure, arteriosclerosis, erectile dysfunction, heart attack and stroke.
Relation between ROS and aging
When ROS damage our cells, lipids in the cell membranes is oxidized, blocking blood vessels. Once the blockage happen, oxygen cannot send nutrients to body tissues anymore, and tissue waste cannot be taken away, either. Also, as vascular cells are damaged and die, oxidized LDL cholesterol forms a firm layer inside blood vessels. This accelerates aging of blood vessels, which then develops arteriosclerosis, erectile dysfunction and other related diseases.
In this way, ROS damage and destroy cells to promote aging of the body and thus gradually cause heart attack, stroke and cancer.
Suppression on ROS can prevent erectile dysfunction
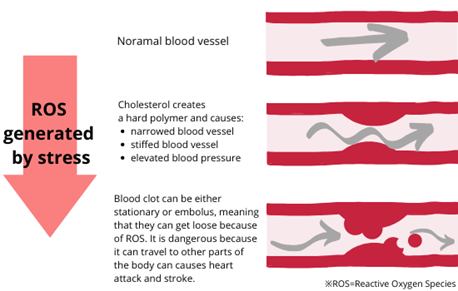
Excessive ROS in blood stack vascular cells and create blockages within blood vessels. The blockage reduce blood flow, inhibiting nutrient and energy from being supplied throughout the body.
Suppressing the ROS that causes blockage is the key to preventing erectile dysfunction.
NOMOA
-The world’s only technology that succeeded in suppressing the occurrence of ROS without medications-

NOMOA was presented as the world’s first successful study to physically suppress ROS in blood at the World Pharmaceutical Congress held in Copenhagen, Denmark in 2010. This was a joint research that had been made by Dr. Naomasa Yamamoto, Dr. Yuichi Koike, Dr. Norifumi Yonehara of Ohu University Faculty of Pharmaceutical Science, and Dr. Katsuyuki Kumano.
First, the study took blood from nine subjects and measured the level of both oxidative stress (ROS / d-ROM) and immunity (BAP) in the sampled blood. The subjects then put their index finger into the device for 10 minutes. After their blood circulated within their body once, blood was sampled to measure oxidative stress level and immunity once again. As a result, all the nine subject’s ROS levels decreased while immunity did not show any decline.
From this result, it was confirmed that NOMOA could suppress ROS in blood without affecting immunity.
To test the sleep-inducing effect on animals, we prepared a miniaturized NOMOA for mice and two mice as subjects.
First, we monitored two mice’s amount of activity with a sensor, which was activated each time the mice moved in a cage. Then, we placed one mouse in the downsized NOMOA for 10 minutes and put it back in the cage for monitoring its amount of activity. The other mouse was left untreated. The amounts of both mice were automatically recorded in the cage for 72 consecutive hours for comparison.
2.7 points was the average amount of activity per minute of the untreated mouse, whereas that of the NOMOA-affected mouse decreased by 7.6% to 48.7 points. From this result, it was demonstrated that the NOMOA-treated mouse had a longer duration of behavioral arrest than the other mouse and that NOMOA caused drowsiness and induced sleep to the mouse as NOMOA successfully suppressed its oxidative stress level (reactive oxygen level) in blood.
The testing also proved that NOMOA could suppress ROS in blood and also prevent ROS-related diseases, such as diabetes, arteriosclerosis, high blood pressure, heart attack and stroke. It also proved that NOMOA could help improving sleep disorders caused by oxidative stress.