What is high blood pressure?
Blood pressure measurement takes into account how much blood is passing through your blood vessels and the amount of resistance the blood meets while the heart is pumping.
Blood pressure is not always constant. It varies depending on the time of day when blood pressure is measured: the season, diet and stress. For example, when you are in a stressful situation, hormones temporarily increase your blood pressure by causing faster heartbeat and narrowing of blood vessels. Although tension or excitement could cause temporary increases in blood pressure, it will normally return to normal levels.
On the other hand, having a high blood pressure means your blood pressure remains high even when you are resting.
High blood pressure measurement
There are four stages of high blood pressure, and each stage has different risks.
| Systolic (mmHg) | Diastolic (mmHg) | ||
| Normal | Less than 120 | and | Less than 80 |
| Elevated | 120-129 | and | Less than 80 |
| High blood pressure Stage 1 | 130-139 | or | 80-89 |
| High blood pressure Stage 2 | 140 or higher | or | 90 or higher |
| Hypertensive crisis | Higher than 180 | and/or | Higher than 120 |
Stage 1 hypertension is a warning sign that you may get high blood pressure in the future. There is no “silver bullet” that can cure high blood pressure entirely, but changes in diet and lifestyle can improve the condition. However, when blood pressure worsens and develops into stage 2 hypertension, medication and other treatments will be required.
Symptoms of high blood pressure
Although some people with high blood pressure might have subjective symptoms, most of them do not have any, which is why it’s called “silent killer.” It is therefore dangerous to think you will hopefully have symptoms to indicate the problem developed inside you. If left unrecognized, the force of your blood pushing against the walls of your blood vessels will remain too high, which may lead to disease such as stroke and heart attack.
To prevent this from happening, it is important to measure your blood pressure regularly.
What causes high blood pressure?
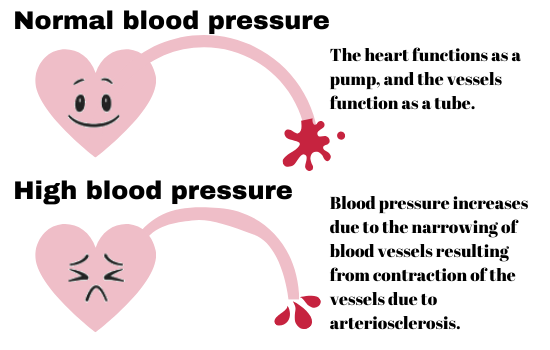
Blood pressure is determined both by the amount of blood your heart pumps and the resistance of blood flow in arteries. The more blood your heart pumps and the narrower your arteries, the higher your blood pressure becomes.
High blood pressure is closely related to lifestyle as well as constitutional factors. It can be caused by a combination of factors such as excess salt, smoking, excess drinking, lack of exercise, stress and aging.
Excess salt
Taking too much salt increases the amount of sodium in the bloodstream and reduces the ability of your kidneys to remove the water. What you get is a high blood pressure due to the extra fluid and extra strain on the delicate blood vessels leading to the kidney.
Stress
When we feel stressed, our body naturally produces hormones that can temporarily increase blood pressure. Those hormones cause faster heartbeat and narrow blood vessels. The longer you feel stressed, the longer it may negatively affect your blood pressure.
Aging
As we age, increase in blood pressure is likely to be associated with structural changes in arteries, such as large-artery stiffness and thinning of blood vessels. It will limit blood flow throughout our body and increases the risk of high blood pressure. Blood vessels contract and expand with temperature, body temperature, and physical condition. However, aging disturbs the function of the autonomic nervous system, causing vascular disease.
Treatment options for high blood pressure
Lifestyle improvement
Most of the time, changes in lifestyle can significantly reduce blood pressure and lower health risks without medications. The changes include:
- Increase activity and exercise
- Control weight
- Eat well-balanced, low-sodium diet
- Limit alcohol use
- Quit smoking
- Manage stress
The above factors not only prevent high blood pressure but also reduce the risk of lifestyle-related diseases.
Medications
There are several medications to lower blood pressure.
- Thiazide diuretics: helps your body to eliminate sodium and water to reduce blood volume
- Vasodilators: opens blood vessels to allow blood to flow more easily
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors: helps relax blood vessels by blocking the action of natural chemical that narrows blood vessels
- Beta blockers: lower blood pressure by reducing heart rate and force of pumping
- Calcium channel blockers: relax blood vessels and reduce heart rate
What causes high blood pressure?
Low-density lipoprotein (bad cholesterol) makes blood vessels stiff and narrow
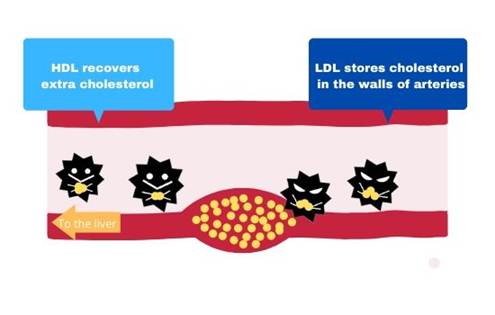
LDL cholesterol enters artery walls to cause arteriosclerosis. The heart acts as a pump to circulate blood through the network of blood vessels, but when blood vessels become stiff and narrow, the pressure cannot be absorbed resulting to high blood pressure.
If this condition continues, the blood vessel wall becomes thicker with cholesterol, so blood cannot circulate through the body, causing higher risks of stroke or heart attack.
The brain needs blood
The brain is an organ that requires a large amount of blood since it is constantly working even when we are asleep. Although the brain is only about 2% of the total body weight, it needs 15-20% of the body’s blood supply. When the vessels become thin, blood flow to the brain is limited as well, which makes brain to send signals to increase blood flow. Doing so will increase the amount of blood pumped from the heart to the entire body, which causes an increase in blood pressure.
When arteriosclerosis progresses, a small stroke may occur, resulting in loss of memory.
Complications triggered by high blood pressure
Cardiac hypertrophy
High blood pressure forces the heart to pump blood harder. To pump harder, the heart muscle becomes thick and make harder for blood to flow smoothly. It also makes it difficult for the heart to relax and pump blood sufficiently.
Cardiac hypertrophy increases the risk of other complications, such as heart failure, ventricular arrhythmias, angina, and heart attack.
Congestive heart failure
Congestive heart failure (CHF) affects the pumping power of the heart muscles. Narrowed arteries or high blood pressure makes the heart too weak or stiff to fill and pump efficiently.
Heart failure may cause symptoms, such as fatigue, shortness of breath, and swelling.
Cerebrovascular disease
About half of the cases of cerebrovascular disease are caused by atherosclerosis because of narrowing and hardening of the arteries, and high blood pressure causes or worsens arteriosclerosis. Once a stroke occurs, brain tissue dies from lack of oxygen and nutrients within an hour, leaving permanent damage on the brain.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) is deeply involved in arteriosclerosis
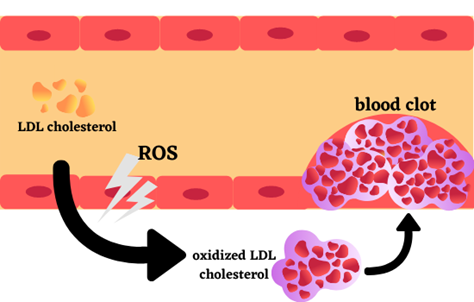
High cholesterol was thought to be the only cause of arteriosclerosis that causes high blood pressure. It was thought that bad cholesterol would enter the blood vessel wall and clog the arteries. However, it has become clear that ROS in the body can also oxidize LDL cholesterol to cause arteriosclerosis.
When our body has too much LDL cholesterol, the excess fat sticks to the inside of the blood vessel walls. The fat thickens the walls and narrows blood vessels, ending up in reduction of blood flow. As the blood vessel wall becomes brittle, blood vessel itself loses elasticity and becomes stiff, leading to further progress of arteriosclerosis.
As you can see, ROS is also the main cause of arteriosclerosis.
Solution to high blood pressure
What is ROS?
When oxygen is carried into the cells of body tissues, it combines with hemoglobin in blood. While moving inside blood vessels, oxygen can be turned to ROS under stress, high level of cholesterol and disorderly oxidized vascular cells. ROS stem from several factors, including lack of exercise, unbalanced diet, stress and habitual smoking, which all develop oxidative stress that causes aging, high blood pressure, arteriosclerosis, heart attack and stroke.
Relation between ROS and aging
When ROS damage our cells, lipids in the cell membranes are oxidized, blocking blood vessels. Once the blockage happens, oxygen cannot send nutrients to body tissues anymore, and tissue waste cannot be taken away, either. Also, as vascular cells are damaged and die, oxidized LSL cholesterol forms a firm layer inside blood vessels. This accelerates aging of blood vessels, which then develops arteriosclerosis, high blood pressure and other related diseases.
In this way, ROS damage and destroy cells to promote aging of the body and thus gradually cause heart attack, stroke and cancer.
Suppression on ROS can prevent high blood pressure
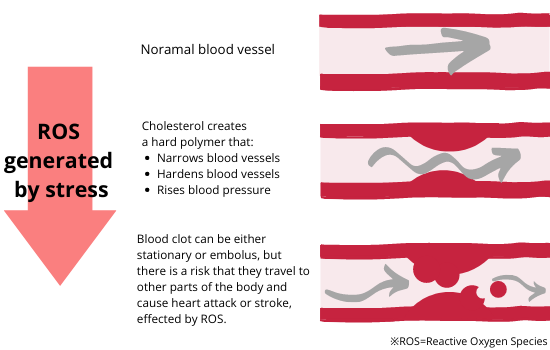
Excessive ROS in blood stack vascular cells and create blockages within blood vessels. The blockage reduce blood flow, inhibiting nutrient and energy from being supplied throughout the body. As the flow is obstructed, blood pressure will rise accordingly.
The key to prevent high blood pressure is to suppress occurrence of ROS, which cause obstruction inside blood vessels.
NOMOA
-The world’s only technology that succeeded in suppressing the occurrence of ROS without medications-

NOMOA was presented as the world’s first successful study to physically suppress ROS in blood at the World Pharmaceutical Congress held in Copenhagen, Denmark in 2010. This was a joint research that had been made by Dr. Naomasa Yamamoto, Dr. Yuichi Koike, Dr. Norifumi Yonehara of Ohu University Faculty of Pharmaceutical Science, and Dr. Katsuyuki Kumano.
First, the study took blood from nine subjects and measured the level of both oxidative stress (ROS / d-ROM) and immunity (BAP) in the sampled blood. The subjects then put their index finger into the device for 10 minutes. After their blood circulated within their body once, blood was sampled to measure oxidative stress level and immunity once again. As a result, all the nine subject’s ROS levels decreased while immunity did not show any decline.
From this result, it was confirmed that NOMOA could suppress ROS in blood without affecting immunity.
To test the sleep-inducing effect on animals, we prepared a miniaturized NOMOA for mice and two mice as subjects.
First, we monitored two mice’s amount of activity with a sensor, which was activated each time the mice moved in a cage. Then, we placed one mouse in the downsized NOMOA for 10 minutes and put it back in the cage for monitoring its amount of activity. The other mouse was left untreated. The amounts of both mice were automatically recorded in the cage for 72 consecutive hours for comparison.
2.7 points were the average amount of activity per minute of the untreated mouse, whereas that of the NOMOA-affected mouse decreased by 7.6% to 48.7 points. From this result, it was demonstrated that the NOMOA-treated mouse had a longer duration of behavioral arrest than the other mouse and that NOMOA caused drowsiness and induced sleep to the mouse as NOMOA successfully suppressed its oxidative stress level (reactive oxygen level) in blood.
The testing also proved that NOMOA could suppress ROS in blood and also prevent ROS-related diseases, such as diabetes, arteriosclerosis, high blood pressure, heart attack and stroke. It also proved that NOMOA could help improve sleep disorders caused by oxidative stress.